Move to Inbox
More
2 of 70,979
LABORATORY AUDIT CHECKLIST

| Jan 2  |
Dear SIR ,
BE PREPARED FOR QMS AUDIT BY ASKING SELF THESE QUESTION .
LABORATORY AUDIT CHECKLIST
1. Safety Equipment | Working | Accessible | Last checked |
a. fume hoods | _________________ | _________________ | _________________ |
b. biological hoods | _________________ | _________________ | _________________ |
c. eye washes | _________________ | _________________ | _________________ |
d. showers | _________________ | _________________ | _________________ |
e. fire extinguisher(s) | A B C D | _________________ | _________________ |
2. House-keeping | Y | N |
a. food, beverages and appliances absent from the laboratory? | _____ | _____ |
b. food absent from chemical refrigerators and vice versa? | _____ | _____ |
c. bench tops clean and unobstructed? | _____ | _____ |
d. emergency numbers posted by telephone? | _____ | _____ |
e. laboratory doors closed? | _____ | _____ |
f. floors, aisles and exits unobstructed? | _____ | _____ |
g outside hallways uncluttered? | _____ | _____ |
3. Chemical Storage | Y | N |
a. all containers appropriately labeled? | _____ | _____ |
b. no flammables in unapproved refrigerators? | _____ | _____ |
c. liquid chemicals equipped with secondary containment? | _____ | _____ |
d. flammable liquids within allowable quantities? | _____ | _____ |
e. chemicals stored appropriately (incompatibles separated)? | _____ | _____ |
f. gas cylinders secured and stored appropriately? | _____ | _____ |
g. empty and full cylinders separated? | _____ | _____ |
4. Waste Management | Y | N |
a. chemical wastes tightly capped? | _____ | _____ |
b. incompatible chemicals separated? | _____ | _____ |
c. liquid chemicals equipped with secondary containment? | _____ | _____ |
d. chemical wastes labeled appropriately? | _____ | _____ |
e. weekly chemical waste inspections documented (where required)? | _____ | _____ |
f. sharps disposed in proper containers? | _____ | _____ |
4. Waste Management (cont.) | Y | N |
i. broken glass disposed in labeled container? | _____ | _____ |
j. radioactive materials disposed in approved containers? | _____ | _____ |
5. Mechanical Equipment | Y | N |
a. guards in place (fans, centrifuges, drive belts)? | _____ | _____ |
b. belts/pulleys in good condition? | _____ | _____ |
6. Electrical Equipment | Y | N |
a. grounded? | _____ | _____ |
b. fitted with overload protection device? | _____ | _____ |
c. outlets located outside of hoods? | _____ | _____ |
d. motors intrinsically safe (where appropriate)? | _____ | _____ |
e. cords in good condition? | _____ | _____ |
f. current carrying parts not exposed? | _____ | _____ |
g. GFIs on outlets within 6 feet of a sink? | _____ | _____ |
7. Paper Work | Y | N |
a. training records available? | _____ | _____ |
b. training records current? | _____ | _____ |
c. training records complete (for all employees)? | _____ | _____ |
d. Incident Report forms available (for work-related illnesses and injuries)? | _____ | _____ |
e. MSDSs accessible? | _____ | _____ |
f. Chemical Hygiene Plan accessible? | _____ | _____ |
g. written laboratory-specific SOPs available? | _____ | _____ |
h. staff knows the laboratory safety officer? | _____ | _____ |
i. Hazardous Chemical Waste Management Guidebook accessible? | _____ | _____ |
j. Radiation Protection Manual accessible? | _____ | _____ |
Is the Laboratory operating under a documented Quality Assurance Program?
• Is the list of all test equipment maintained with serial numbers, and calibration
due dates?
• Is the independent calibration of equipment traceable to nationally recognized
standards when appropriate
• Is the lab only performing tests that are covered in the scope of accreditation?
• Is the Laboratory operating under a documented Safety Control Program?
• Are records of relevant training, skills, and experience of the technical
personnel being maintained?
• Are records of tests performed being kept for the minimum 10 years as
required?
Microbiology Laboratory Audit Check List- Facilities Yes | No | SOP /Document No. | Remarks |
Is there an adequate space for all the activities performed in the laboratory? | |||
Is there an orderly placement of equipment, Instruments, and materials to prevent mix-up and cross contamination? | |||
Are there dedicated areas for the following? • supplies receipt, and storage? • sample receipt, storage and testing • media preparation, and storage • microbial purity testing • sterility testing • handling and identification of microorganisms • personnel offices • break room • biohazard material | |||
Are the work surfaces, walls, and floors smooth, free of cracks and easy to clean? | |||
Is the laboratory furniture made of non-porous materials that are easily cleaned? | |||
Is there a formal cleaning program in place that includes cleaning and disinfection of overhead ducts, pipes, light fixtures, sinks, cabinets, bench tops, furniture, walls, floors, ceiling, workbenches and trash cans? | |||
Are the disinfectants used in the laboratory qualified and the expiration dates for the prepared solution validated? | |||
Is there a formal program in place to assess the air quality and surfaces in the general laboratory area? | |||
Are alert and action levels established for air quality and surfaces? | |||
Is the frequency of environmental monitoring based an initial facility | |||
qualification data? | |||
Are environmental monitoring data generated routinely reviewed, trended, and checked for excursions? | |||
Is there a requirement to perform investigation of out of trend (OOT) or out of alert/action (OOA) environmental monitoring data? | |||
Is there a requirement for characterization of microbial isolates from the general laboratory environment to establish a valid database , and to demonstrate effectiveness of the cleaning and disinfection procedures | |||
Is there a system in place to control traffic in the laboratory? | |||
Is the temperature in the general laboratory area controlled and monitored? | |||
Is the temperature and humidity in the media storage area controlled and monitored? | |||
Is there a dress code for laboratory personnel as well as visitors? | |||
Are activities appropriately segregated to prevent mix-ups and cross-contamination? | |||
Are biohazard waste and contaminated glassware segregated in an area that is clearly labeled as containing biohazard materials? | |||
Is there a validated decontamination process for biohazard material prior to disposal or cleaning? | |||
Are clean glassware segregated in an area clearly labeled as such? | |||
Is there a requirement not to store cardboard boxes in the laboratory? | |||
Is there a requirement for containment, i.e., to close all cabinet doors, and doors leading to the general laboratory area, and the sterility suite? | |||
Are trash cans emptied on a daily basis? | |||
Is the daily cleaning and disinfection activities recorded, and reviewed for accuracy and completeness? | |||
Are safety signs posted in the laboratory? | |||
Are there procedures in place to address the following? • cleaning and house-keeping practices for the general laboratory area • handling of biohazard waste and materials • dress code for the laboratory | |||
• handling of chemicals and biological spills • cleaning of glassware • monitoring of temperature, humidity and air and surface quality • control of traffic | |||
With best regards,
(2015)
Dr. AMAR NATH GIRI(2015)
M.Sc. -Environmental Science,Ph.D -Environmental Science law& DIPLOMA AS - P.G.D.E.P.L,CES, DCA,
EX IIM LUCKNOW FELLOW, EX RESEARCH SCIENTIST
IGIDR-MUMBAI
9912511918
amarnathgiri@nagarjunagroup.
http://www.nagarjunagroup.com
http://www.
http://dramarnathgiri.
http://dramarnathgiri.

|  6:59 AM (3 minutes ago) 6:59 AM (3 minutes ago) |
| |||
3 Attachments
People (4)
|
Recent photos Show details |
 Promoting a positive environmental image with customers, and increasing demand for products and services;
Promoting a positive environmental image with customers, and increasing demand for products and services;  An environmental policy supported by senior management;
An environmental policy supported by senior management;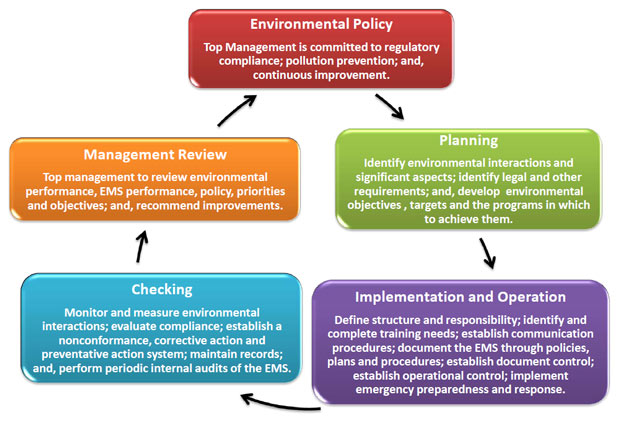
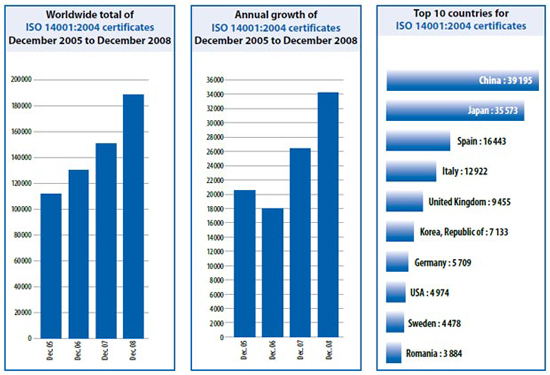


 The Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) is an organisational management tool for the evaluation, reporting and continuous improvement of environmental performance. The scheme has been successfully integrated into many business types in the EU where it is defined in legislation and the uptake is on a voluntary level.
The Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) is an organisational management tool for the evaluation, reporting and continuous improvement of environmental performance. The scheme has been successfully integrated into many business types in the EU where it is defined in legislation and the uptake is on a voluntary level. 






























