Top Three Indian Languages After Hindi
By Sarah-Claire Jordan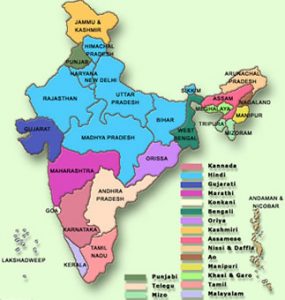 India is a country with such interesting history that it is definitely feasible that it would be home to many different languages. As of 2001, there are about 122 languages in India that are considered “major languages”, with over 1,500 other languages. Though the Constitution of India only lists Hindi and English as the official languages (and doesn’t designate a national language), over 20 other languages have government recognition and status. Hindi (and often English) is used as lingua franca in India, as different languages are spoken in different regions.
India is a country with such interesting history that it is definitely feasible that it would be home to many different languages. As of 2001, there are about 122 languages in India that are considered “major languages”, with over 1,500 other languages. Though the Constitution of India only lists Hindi and English as the official languages (and doesn’t designate a national language), over 20 other languages have government recognition and status. Hindi (and often English) is used as lingua franca in India, as different languages are spoken in different regions.Anyone familiar with India will tell you that Hindi is the most popular language in India in terms of number of speakers. This is seen in the extensive use of Hindi in Bollywood movies, music, and more. However, not many people know much about the other commonly spoken languages of India. Here are the top three languages spoken in India, after Hindi.
1. Bengali
Bengali, also called Bangla, originated in the Bengal region of India, which is now made up of Bangladesh and the Indian states of Tripura, West Bengal, and the southern part of the state of Assam. It has its own alphabet, the Bengali alphabet, that is used to write the language. The National Anthem of India was originally composed in Bengali, which gives you an idea of the impact it has on the country. It is part of the Indo-European language family, like the majority of languages from India. There are numerous dialects of Bengali which are divided into four clusters or groups. There is even an entire film industry that makes movies in the Bengali language, known as Tollywood. It was around even before Bollywood, whose name was actually inspired by Tollywood.
2. Telugu
Coming in third behind Hindi and Bengali as the most common language spoken in India is Telugu. Telugu is one of the few Dravidian languages spoken in India and is spoken in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Yanam as well as in surrounding areas. It is included in the group of six languages in India that are considered classical languages of the country. The first written records of Telugu have been dated back to between 400 and 100 BC, lending credibility to its position among other classical Indian languages. There are over twenty different dialects of Telugu spoken in different parts of India. Telugu, like Bengali, has its own alphabet, and Telugu words tend to end in vowels.
3. Marathi
Marathi is the 19th most spoken language in the world, and the fourth most common native language in India. It has some of the oldest examples of literature of the Indo-Aryan languages still spoken in India, which were written back in 900 AD. In the state of Maharashtra, Marathi is considered the official language, as well as sharing the title with other languages in some neighboring states. The Marathi writing system uses an adaptation of the Devanagari alphabet, which is called Balbodh, though before the middle of the 1900s it was written using the Modi script. Marathi has about five different major dialects, with many minor ones that have a high level of mutual intelligibility.