Pretreatment
Pretreatment Selection
1. Remove suspended solids.
2. Control calcium scaling.
* Antiscalant Injection
* Softening
* pH Adjustment (Acid Injection)
3. Other treatment as dictated by water analysis and desired recovery.
| Particulate | 10 to 25 micron cartridge filter. Sand or diatomaceous earth filter (Optional) |
| pH correction | Acid addition to lower pH to about 6. Membrane hydrolysis function of pH |
| Calcium Carbonate | pH adjustment prevents precipitation |
| Calcium Sulfate | Precipitation inhibited with scale inhibitors |
| Iron & Manganese | Soluble state no problem, but dander is oxidation to insoluble form at or near membrane. Oxidation, reduction, scale inhibitor possible methods |
| Colloids | Coagulation/Flocculation; Ultrafiltration |
| Organic Deposits | Filtration, Activated Carbon, Polyelectrolytes |
| Microbiological Organisms | Chlorination |
| Silica | Dependent on form, soluble, crystalline amorphous |
| Temperature | Product flux µ temperature; 1 to 1.5% per degree |
Pretreatment Techniques
| Feed Water Characteristics | Potential | Treatment |
| Turbidity (Suspended solids) | Forms Deposits in lines and equipment | Coagulation, settling, filtration |
| Color | Stains and causes foaming | Coagulation, filtration absorption |
| Odor (see dissolved gases) | Chlorination, Absorption | |
| Taste | Chlorination, Absorption | |
| Chemical Characteristics | Potential | Treatment |
| Hardness (Ca and Mg salts) | Forms Scale | pH, softening, conversion control |
| Minerals (Na, K, CI, SO4, HCO3) | Contribute to TDS | RO |
| Mn++ | Forms Deposits | Oxidation |
| Fe++ | Upon Oxidation | Filtration |
| Silica | Forms Scale | Lime softening process |
| Gases (O2 , H2 S, CO2 , NH3) | Cause Corrosion | Aeration Degasification |
| Biological Characteristics | Potential | Treatment |
| Bacteria | Forms organic | Chlorination |
| Algae | Deposits | UV Irradiation |
| Viruses |
Summary of Pretreatment Options
This table summarizes the pretreatment options when specific risks for scaling and fouling are present. It is a quick reference for "possible" and "very effective".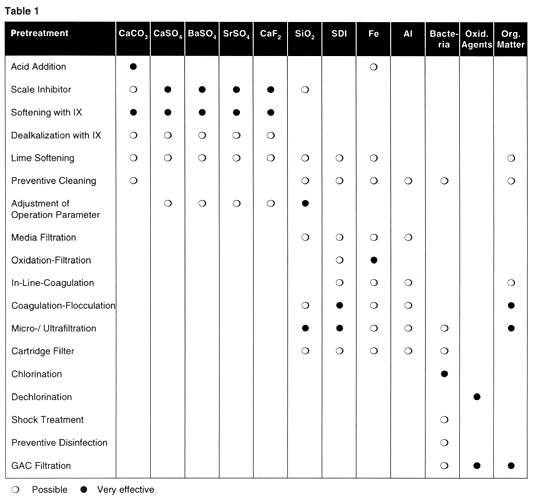
Dechlorination
- Sodium Bisulfite (Na H SO3)
-10% Solution
-3 Lbs. of Na H SO3 per lb. of Cl2
- Activated Carbon
-1 million PPM gallons per cubic ft.
- Solution life of Sodium Bisulfite
SODIUM BISULFITE SOLUTION WEIGHT % | MAXIMUM SOLUTION LIFE |
2 | 3 Days |
10 | 1 Week |
20 | 1 Month |
30 | 6 Months |
Activated Carbon
- 1 cubic foot of Carbon will remove 1 ppm of Chlorine from 1 million gallons of water
- Design Flow Rate
-Chlorine 15 gpm/ft2
-Organics 6 gpm/ft2
Removal of Suspended Solids
| Technique | Equipment Options |
| Gravity Separation | Primary Sedimentation Secondary Sedimentation Chemical Sedimentation Flotation Clarification Settler |
| Physical Straining Process | Screening Diatomaceous Earth Filtration Ultrafiltration |
| Granular Media Filtration | Upflow Sand Filters Downflow Sand Filters Green Sand Filters Multi Media Filters Special Design Filters |
Granular-Media Deep-Bed Filtration
Table V. Minimum Fluidization Velocities for Various Uniform-Sized Media
(Observed Empirically)9
Between U.S. Std. Sieves
| Passing | Mm | Retained | Size | Mean Flow Rate to Achieve 10% | ||
| (mm) | Expansion at 25°C, gpm/ft2 | |||||
| Coal | Sand | Garnet | ||||
7 | 2.830 | 8 | 2.59 | 37.0 | ||
8 | 2.380 | 10 | 2.18 | 30.0 | ||
10 | 2.000 | 12 | 1.84 | 24.0 | 41.0 | |
12 | 1.680 | 14 | 1.54 | 20.0 | 33.0 | |
14 | 1.410 | 16 | 1.30 | 15.7 | 27.0 | 49.0 |
16 | 1.190 | 18 | 1.09 | 12.5 | 21.0 | 40.0 |
18 | 1.000 | 20 | 0.92 | 9.9 | 16.4 | 32.0 |
20 | 0.841 | 25 | 0.78 | 8.4 | 12.6 | 27.0 |
25 | 0.707 | 30 | .65 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 22.0 |
30 | 0.595 | 35 | 0.55 | 6.3 | 18.0 | |
35 | 0.500 | 40 | 0.46 | 5.4 | 13.7 | |
40 | 0.420 | 45 | 0.38 | 4.0 | 11.3 | |
50 | 0.297 | 60 (.25mm) | 0.27 | 6.3 | ||
Specify Gravity | 1.7 | 2.65 | 4.1 | |||
Table VI. Temperature Correction: Approximate Correction Factors to be Applied for Temperatures Other Than 25°C
Temperature (°C) | Multiply the 25°C Value by |
30 | 1.09 |
25 | 1.00 |
20 | 0.91 |
15 | 0.83 |
10 | 0.75 |
5 | 0.68 |
Typical Pressure Filter Media Beds For RO Pretreatment
A. SAND FILTERS
Top Layer -12” to 24” fine sand -0.45 to 0.6 mm e.s.
Middle Layer -6” to 12” coarse sand -0.8 to 1.2 mm e.s.
Bottom Layer -4” find gravel -1/4” to 1/8” diam.
B. DUAL - MEDIA FILTERS
Top Layer -6” to 24” No. 1 anthrafilt -0.65 to 0.76 mm e.s.
Layer -12” to 18” fine sand -0.45 to 0.6 mm e.s.
Layer -6” coarse sand -0.8 to 1.2 mm e.s.
Bottom Layer -4” fine gravel -1/4” to 1/8” diam.
C. MANGANESE ZEOLITE FILTERS
Top Layer -0 to 6” No. 1 anthrafilt -0.65 to 0.76 mm e.s.
Layer -12” to 18” manganese zeolite -0.27 to 0.37 mm e.s.
Layer -4” to 6” fine sand -0.45 to 0.6 mm e.s.
Layer -0 to 6” coarse sand -0.8 to 1.2 mm e.s.
Bottom Layer -4” fine gravel -1/4” to 1/8” diam
NOTE: Bed depths will depend on available height of pressure filter and at least 50% of bed depth should be allowed as free board for bed expansion.
Deep Bed Filtration - Design Recommendations
DUAL MEDIA
Recommended Depth:
Coal 18” - 24”
Sand 15” - 18”
FILTRATION RATE
5 Gallons/Minute/Square Foot Dual Media
15 Gallons/Minute/Square Foot Multi Media