Quality Management Systems: Logistics, Risks and Monitoring
![quality management]()
As organizations grow the expansion of the supplier base creates the need for quality management in logistics. Globalization and outsourcing of products and services have created a daisy chain supply chain with longer lead times, more pipeline inventory and the need for logistics control over items coming in and items going out. Establishing a supply chain network includes supplier selection and the movement of goods and services to the customer.
Quality management audit programs do not develop the supply chain networks, but they do verify and monitor activities to make sure that the requirements are met.
Movement of goods and services include modes of travel—train, roadway, sea and air, distribution and storage services; storage conditions; technical services, expedited services and controlling storage costs and expenses like detention and demurrage fines. Supplier selection includes initial evaluation, maturity model results and assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
Risks
As supply chains stretch across the globe, there are going to be different risks. In spite of risks deadlines must be met and customers satisfied. If there are language and cultural barriers, these must be overcome since communication is an important aspect for succeeding. Electronic audits are becoming viable options and an important quality management audit program strategy ensuring proper oversight and control of risks.
Risk is something quality management is always concerned about. They have been taught to avoid unnecessary risks. Using the ISO 9000 standards and similar sector-specific standards are strategies designed to reduce risks in certain areas like product liability, environment controls, occupational safety and health.
Since fewer business processes are being controlled within the business, there is a greater need to manage supply chain risks. This creates a difficult situation as increasing dependence on supplier organizations increase a customer’s business risk. Quality management risk scope includes controls throughout the product’s life cycle, across all organizational processes and its external supply chain. So the scope of a program might be limited to product or might include selected enterprise processes.
The purpose of the program is to ensure that customer requirements are met and to prevent external product failures and nonconformities. The effective quality management risk program reduces the chances of failures with their monetary consequences for the organization.
With no risk management system in place the organization is in a constant reaction mode exposing it to surprise problems and containment instead of problem solving. With a risk management program the organization can be proactive in eliminations problems before they happen.
The benefits of a risk management system to the organization include:- Reduced probability of delivering nonconforming products and services.
- Increased probability of achieving organizational objectives.
- Reduced probability of delivering product or services behind schedule.
- Increased probability of compliance to quality, environmental and safety regulations, plus the avoidance of undesirable consequences.
When the risks are properly identified and treatments imposed, the audit function may be to verify that the risks are indeed controlled and treated. An auditor and audit program quality managers do not assess identified risks unless they are specifically assigned to the team for that purpose.
Monitoring
When an auditor visits with a supplier, he has a duty to report any potentially significant risks to the audit program manager and the client. If the risk is of a certain critical level, it may be necessary for the auditor to monitor the supplier. Monitoring and reporting needs will change as the organization’s needs change and relationships with supplies change.
Monitoring and verification include:- Assessment of capabilities.
- Source inspection.
- Ongoing inspection (100% inspection, acceptance and skip lot inspection).
- Certification of conformance.
- Surveys.
- A conformity audit.
- A contract audit.
- A risk-based audit.
- Verification of corrective actions.
External auditors may need additional training in working with different cultures. If there is a misunderstanding, it can delay the audit or damage the business relationship. External auditors also need to have technological knowledge about the parts and processes that go into creating the product.
Audit results are one part of maintaining an effective supplier relationship. The results might be the basis for increasing or decreasing the need for oversight of the supplier organization. The higher the supplier level, the less oversight is needed.

 Radioactivity:
Radioactivity:

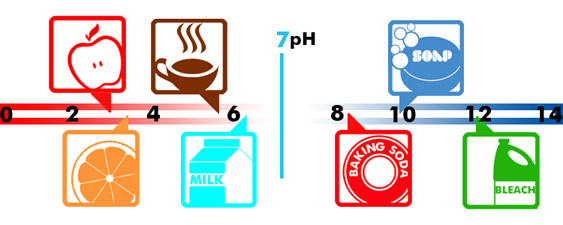

 However, some other cells may adapt in that environment. In other words, instead of dying - as normal cells do in an acid environment - some cells survive by becoming abnormal cells. These abnormal cells are called malignant cells. Malignant cells do not correspond with brain function or with our own DNS memory code. Your body's pH level is a large indicator of your alkalinity.
However, some other cells may adapt in that environment. In other words, instead of dying - as normal cells do in an acid environment - some cells survive by becoming abnormal cells. These abnormal cells are called malignant cells. Malignant cells do not correspond with brain function or with our own DNS memory code. Your body's pH level is a large indicator of your alkalinity.  Most adults will lose between two to three quarts of water per day by way of normal body functions, but those who live in or work in warmer environments tend to lose more. Athletes for example, need to drink more water to balance their bodily fluids. For those people, drinking more water will make up for the bigger loss of water they had through perspiration, as well as in the regulation of body temperature.
Most adults will lose between two to three quarts of water per day by way of normal body functions, but those who live in or work in warmer environments tend to lose more. Athletes for example, need to drink more water to balance their bodily fluids. For those people, drinking more water will make up for the bigger loss of water they had through perspiration, as well as in the regulation of body temperature.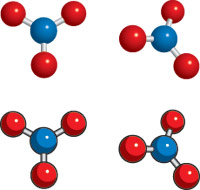 Pure water consists almost entirely of H2O molecules loosely bound in a network-like structure in which individual molecules are constantly changing partners. Water molecules exhibit a very slight tendency to dissociate ("ionize") into hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions: H2O ; H+ + OH- but the extent of this reaction is severely limited by the fact that the reverse of this reaction is much more rapid, so that on the average, only about two out of every billion H2O molecules is dissociated. No electrical device or chemical additive is capable of increasing these ion concentrations in pure water above this very minute level which is so small that for most practical purposes pure water can be considered to be ion-free, as evidenced by the fact that it will not conduct an electric current.
Pure water consists almost entirely of H2O molecules loosely bound in a network-like structure in which individual molecules are constantly changing partners. Water molecules exhibit a very slight tendency to dissociate ("ionize") into hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions: H2O ; H+ + OH- but the extent of this reaction is severely limited by the fact that the reverse of this reaction is much more rapid, so that on the average, only about two out of every billion H2O molecules is dissociated. No electrical device or chemical additive is capable of increasing these ion concentrations in pure water above this very minute level which is so small that for most practical purposes pure water can be considered to be ion-free, as evidenced by the fact that it will not conduct an electric current. 
 Velocity. Because of the greater amount of competition you want to release products more quickly than you did a few years ago. This velocity is driving shortened time-to-market that then drives shorter sales cycles and higher revenues. Velocity means you have to improve the operational efficiencies when it comes to document publication more rapidly. Your new and improved product needs new and improved content which you need to publish more rapidly and accurately to be ready for the customer.
Velocity. Because of the greater amount of competition you want to release products more quickly than you did a few years ago. This velocity is driving shortened time-to-market that then drives shorter sales cycles and higher revenues. Velocity means you have to improve the operational efficiencies when it comes to document publication more rapidly. Your new and improved product needs new and improved content which you need to publish more rapidly and accurately to be ready for the customer. http://www.yourstylishlife.com/how-to-purify-your-lungs-in-72-hours/
http://www.yourstylishlife.com/how-to-purify-your-lungs-in-72-hours/









