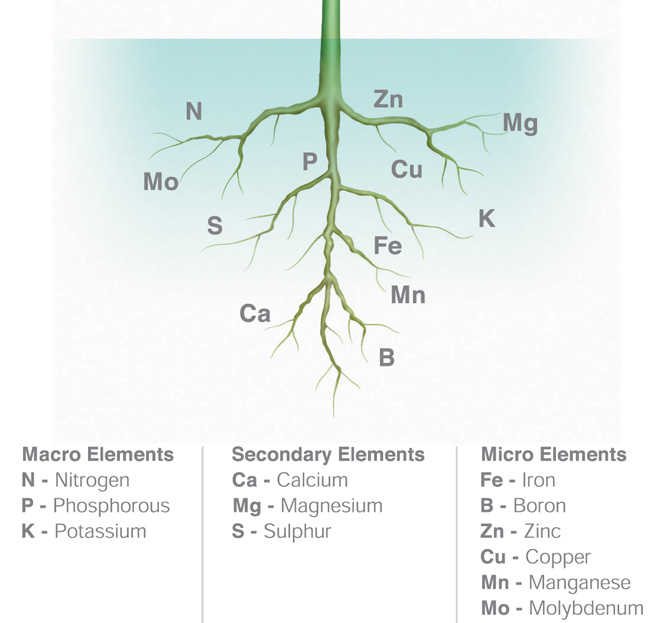

Nutrients are classified into:
- Primary Nutrients (Phosphorous, Nitrogen, Potassium)
- Secondary Nutrients (Calcium, Magnesium, Sulphur)
- Micronutrients (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cl, Mo, B, Se)
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is required by every living plant and animal cell. It is vital for plants energy synthesis, storage and transfer. It is an important component of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which generates energy for the plant. Phosphorous influences early root development and is irreplaceable for the development of tissues that form a plant’s growing points. Phosphorous helps plants to survive temperature changes and water deficiency and is fundamental to the successful development of all crops. Phosphorous improves the quality of grain and accelerates its ripening.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is involved in all major processes of plant development. It is a driver of plant growth. Nitrogen is used in protein synthesis and chlorophyll production which gives plants its dark green color. When nitrogen is deficient, plants develop a yellow or pale colour and their growth slows. Nitrogen is involved in regulating the uptake of other nutrients and elements. It is taken up in larger amounts than other nutrients.
Potassium
Potassium regulates the plant’s water regime and increases tolerance to drought, frost and salinity. Nitrogen uptake of plant is tightly connected with potassium content. Potassium is a key component in cell wall strength and plants resistance to disease.
]