Humidex Rating and Work
What is humidex?
Humidex is a measure of how hot we feel. It is an equivalent scale intended for the general public to express the combined effects of warm temperatures and humidity. It provides a number that describes how hot people feel, much in the same way the equivalent chill temperature, or "wind chill factor," describes how cold people feel. Humidex is used as a measure of perceived heat that results from the combined effect of excessive humidity and high temperature.
Environment Canada uses humidex ratings to inform the general public when conditions of heat and humidity are possibly uncomfortable.
Environment Canada uses humidex ratings to inform the general public when conditions of heat and humidity are possibly uncomfortable.
| Table 1 | |
|---|---|
| Humidex Range | Degree of Comfort |
| 20-29 | comfortable |
| 30-39 | some discomfort |
| 40-45 | great discomfort; avoid exertion |
| above 45 | dangerous; heat stroke possible |
What is the importance of humidity?
The body attempts to maintain a constant internal temperature of 37°C at all times. In hot weather, the body produces sweat, which cools the body as it evaporates. As the humidity or the moisture content in the air increases, sweat does not evaporate as readily. Sweat evaporation stops entirely when the relative humidity reaches about 90 percent. Under these circumstances, the body temperature rises and may cause illness.
What are some of the hazards of working in hot environments?
There are several common heat-related illnesses. Some are more severe than others.
Heat rash, or prickly heat, occurs when blocked sweat glands become inflamed. This painful rash reduces the body's ability to sweat and to tolerate heat.
Heat cramps are painful spasms of the muscles. The muscles used in doing the work are most susceptible. The spasms are caused by the failure of the body to replace its lost body salts and usually occur after heavy sweating.
Heat exhaustion results when the body loses large amounts of fluid by sweating during work in hot environments. The skin becomes cool and clammy. Symptoms include profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headaches.
Heat stroke is the most serious condition and requires immediate medical attention. The body temperature becomes very high (even exceeding 41°C). Complete or partial loss of consciousness is possible. Sweating is not a good symptom of heat stress as there are two types of heat stroke -- "classical" where there is little or no sweating (usually occurs in children, persons who are chronically ill, and the elderly), and "exertional" where body temperature rises because of strenuous exercise or work and sweating is usually present.
Heat rash, or prickly heat, occurs when blocked sweat glands become inflamed. This painful rash reduces the body's ability to sweat and to tolerate heat.
Heat cramps are painful spasms of the muscles. The muscles used in doing the work are most susceptible. The spasms are caused by the failure of the body to replace its lost body salts and usually occur after heavy sweating.
Heat exhaustion results when the body loses large amounts of fluid by sweating during work in hot environments. The skin becomes cool and clammy. Symptoms include profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headaches.
Heat stroke is the most serious condition and requires immediate medical attention. The body temperature becomes very high (even exceeding 41°C). Complete or partial loss of consciousness is possible. Sweating is not a good symptom of heat stress as there are two types of heat stroke -- "classical" where there is little or no sweating (usually occurs in children, persons who are chronically ill, and the elderly), and "exertional" where body temperature rises because of strenuous exercise or work and sweating is usually present.
Can workplaces use humidex to monitor conditions that may result in heat-related illness?
Humidex as reported by weather forecasters is intended for the general public to express the combined effects of warm temperatures and humidity.
Heat-related illnesses depend on many workplace factors in addition to air temperature and humidity. Wind speed or air movement, work load, radiant heat sources and a person's physical condition are also important.
Under certain workplace conditions, the humidex may serve as an indicator of discomfort resulting from occupational exposures to heat.
For example, when humidity is high, but when work load, wind speed and radiant heat sources do not significantly contribute to the heat burden, humidex may be useful. Offices are typical of workplaces where humidex could be used. It is important to use the values of the temperature and relative humidity obtained by actual measurements taken in the workplace. Conditions inside the workplace may significantly differ from those given by the Weather Service.
Heat-related illnesses depend on many workplace factors in addition to air temperature and humidity. Wind speed or air movement, work load, radiant heat sources and a person's physical condition are also important.
Under certain workplace conditions, the humidex may serve as an indicator of discomfort resulting from occupational exposures to heat.
For example, when humidity is high, but when work load, wind speed and radiant heat sources do not significantly contribute to the heat burden, humidex may be useful. Offices are typical of workplaces where humidex could be used. It is important to use the values of the temperature and relative humidity obtained by actual measurements taken in the workplace. Conditions inside the workplace may significantly differ from those given by the Weather Service.
How do I know what the humidex is?
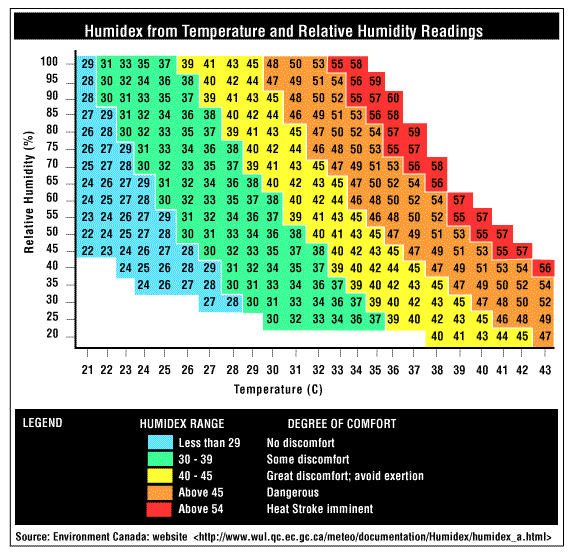
If you know the temperature and relative humidity, the following chart can be used to determine the humidex rating. For example, if the temperature is 30°C and the relative humidity is 70%, the humidex rating is 41. This level is considered a level of "great discomfort" and exertion should be avoided.
Table 2
![Table 2 - Humidex from temperature and relative humidity readings]()
How is humidex interpreted?
The relation between humidex and comfort is subjective. It varies widely between individuals.
Workplaces must use caution when applying the humidex. A high humidex can serve as a cue to assess workplace conditions more precisely. The following are some examples of guidelines used by various agencies for office work:
While technically there is no way to directly compare WBGT and humidex values, this humidex response plan provides an additional guideline that uses information that is easily available to most employers. OHCOW notes, "in the translation process some simplifications and assumptions have been made, therefore, the plan may not be applicable in all circumstances and/or workplaces (follow steps 1 through 5 to ensure the humidex plan is appropriate for your workplace)" which is available on their website at Source: Occupational Health Clinics for Ontario Workers (OHCOW) - Humidex Based Heat Response Plan.
See Table 3 for details.
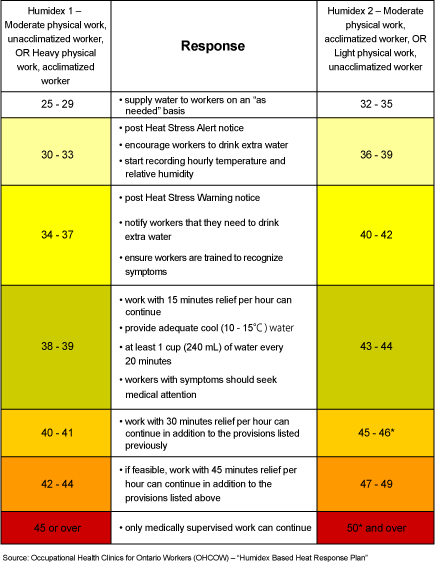
Notes: These humidex levels are for unacclimatized workers performing moderate physical activity. The ACGIH specifies an action limit and a TLV® to prevent workers' body temperature from exceeding 38°C (38.5°C for acclimatized workers). Below the action limit (Humidex 1 for work of moderate physical activity) most workers will not experience heat stress. Most healthy, well-hydrated, acclimatized workers not on medications will be able to tolerate heat stress up to the TLV®. (Humidex 2 for moderate physical activity). Between Humidex 1 and Humidex 2, general heat stress controls are needed and above Humidex 2 job-specific controls are needed.
Workplaces must use caution when applying the humidex. A high humidex can serve as a cue to assess workplace conditions more precisely. The following are some examples of guidelines used by various agencies for office work:
- The Public Works Canada guideline, "Environmental standards for office accommodation," recommends a minimum temperature of 20°C when heating and a maximum temperature of 26°C when cooling.
- The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) Standard 55-2010 "Thermal environmental conditions for human occupancy" recommends temperature ranges of 20°C to 26°C at 50% relative humidity as comfortable for sedentary work. An air temperature of 26°C at 50% relative humidity corresponds to a humidex of 29.
While technically there is no way to directly compare WBGT and humidex values, this humidex response plan provides an additional guideline that uses information that is easily available to most employers. OHCOW notes, "in the translation process some simplifications and assumptions have been made, therefore, the plan may not be applicable in all circumstances and/or workplaces (follow steps 1 through 5 to ensure the humidex plan is appropriate for your workplace)" which is available on their website at Source: Occupational Health Clinics for Ontario Workers (OHCOW) - Humidex Based Heat Response Plan.
See Table 3 for details.
Notes: These humidex levels are for unacclimatized workers performing moderate physical activity. The ACGIH specifies an action limit and a TLV® to prevent workers' body temperature from exceeding 38°C (38.5°C for acclimatized workers). Below the action limit (Humidex 1 for work of moderate physical activity) most workers will not experience heat stress. Most healthy, well-hydrated, acclimatized workers not on medications will be able to tolerate heat stress up to the TLV®. (Humidex 2 for moderate physical activity). Between Humidex 1 and Humidex 2, general heat stress controls are needed and above Humidex 2 job-specific controls are needed.
Table 3
Recommended Actions Based on the Humidex Reading
![Table 3 - Recommended Actions Based on the Humidex Reading]()
Recommended Actions Based on the Humidex Reading
What index should workplaces use to monitor conditions that may result in heat-related illness?
Occupational (Industrial) hygienists recommend using the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) index to measure workplace conditions. This method closely relates to the human body's response to heat.
The WBGT measurement takes into account air temperature, air movement, radiant heat and humidity. There are direct-reading WBGT meters. These are also called "heat-stress indicators," commercially available. The WBGT measurements can then be related to the physical demands of the job. Only qualified professionals, whether they be in-house staff, consultants, or from the local occupational health and safety regulatory agency, should perform the measurement.
Direct comparison between WBGT and humidex is not possible--there are no conversion tables or mathematical formulas to do such conversions. However, one can estimate WBGT and humidex for a given ambient air temperature and humidity when radiant heat sources (hot and cold surfaces) are absent and air movement is less than 0.5 m/sec. (100 feet per minute). Under these conditions the globe temperature equals room temperature and the natural wet bulb temperature (on the WBGT apparatus) is approximately 2°F (1.1°C) higher than the wet bulb temperature measured using a psychrometer.
Standard charts are available to determine wet bulb temperature from given air temperature and relative humidity values. For indoor or outdoor conditions with no direct sunlight, WBGT is calculated by using the following formula:
The WBGT measurement takes into account air temperature, air movement, radiant heat and humidity. There are direct-reading WBGT meters. These are also called "heat-stress indicators," commercially available. The WBGT measurements can then be related to the physical demands of the job. Only qualified professionals, whether they be in-house staff, consultants, or from the local occupational health and safety regulatory agency, should perform the measurement.
Direct comparison between WBGT and humidex is not possible--there are no conversion tables or mathematical formulas to do such conversions. However, one can estimate WBGT and humidex for a given ambient air temperature and humidity when radiant heat sources (hot and cold surfaces) are absent and air movement is less than 0.5 m/sec. (100 feet per minute). Under these conditions the globe temperature equals room temperature and the natural wet bulb temperature (on the WBGT apparatus) is approximately 2°F (1.1°C) higher than the wet bulb temperature measured using a psychrometer.
Standard charts are available to determine wet bulb temperature from given air temperature and relative humidity values. For indoor or outdoor conditions with no direct sunlight, WBGT is calculated by using the following formula:
WBGT = 0.3 x globe temperature + 0.7 x natural wet bulb temperature