Correcting concentrations for altitude
Atmospheric pollutant concentrations expressed as mass per unit volume of atmospheric air (e.g., mg/m³, µg/m³, etc.) at sea level will decrease with increasing altitude because the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude.The change of atmospheric pressure with altitude can be obtained from this equation:[2]
- Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
- Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
| where: | |
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view. 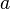 | = altitude, in hundreds of meters |
|---|---|
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view.  | = atmospheric pressure at altitude Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view. 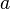 , in atmospheres , in atmospheres |
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view.  | = Concentration at sea level altitude, in mass per unit volume |
| Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view.  | = Concentration at altitude Image may be NSFW. Clik here to view. 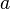 , in mass per unit volume , in mass per unit volume |
Ca = 260 × 0.9877 18 = 208 mg/m³ at 1,800 meters altitude


