Nutrient Management
| Nitrogen | |
 |
|
| Phosphorus | |
|  |
| Potassium | |
 |
|
| Calcium | |
|  |
| Magnesium | |
 |
|
| Sulphur | |
|  |
| Iron | |
 |
|
| Zinc | |
|  |
| Boron | |
 |
|
| Copper | |
|  |
| Manganese | |
 |
|
| Silicon | |
|  |
| Top |
| Nutritional Disorders |
| Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities |
| Nitrogen | |
   | Deficiency Symptoms
Corrective measures
Nitrogen sources Farmyard manure, Green manures, Biofertilizers (Rhizobium, AzollaAzospirillum, Azotobacter) Castor cake, Neem cake, Urea, Diammonium phosphate, Ammonium nitrate, Ammonium sulphate. |
| Phosphorus | |
Deficiency symptoms
Corrective measures
Phosphorus sources: Farmyard manure, Biofertilizers (Phosphate solubilizers) Castor cake, Neem cake,Super phosphate (single),Super phosphate (Double),Super phosphate (Triple), Basic slag, Mussori, Diammonium phosphate (SPIC), Ammonium phosphate (Gromor) Phosphorus toxicity (Injury due to excess P application) 1. Fixed in soil – not available to plants 2. Leads to Zinc deficiency |   |
| Potassium | |
  | Deficiency symptoms
Corrective measures:
Potassium sources Farmyard manure, Castor cake, Neem cake, Muriate of potash (KCl), Potassium sulphate Injury due to excess K application
|
| Calcium | |
Deficiency symptoms
Corrective measures:
Calcium sources: Farmyard manure, Calcium chloride. Gypsum, dolomite, lime, pyrites, single superphosphate or triple superphosphate. |  |
| Magnesium | |
 | Deficiency symptoms:
Magnesium sources: Farmyard manure, Magnesium chloride, dolomite. |
| Sulphur | |
Deficiency symptoms:
Corrective measures:
Sulphur sources: Ammonium sulfate, Single superphosphate, Potassium sulfate, gypsum and S-coated urea. |   |
| Iron | |
  | Deficiency symptoms:
Corrective measures:
Iron sources: Soluble ferrous sulfate (20-33% Fe), ferrous ammonium sulfate (14% Fe), and iron chelates (5 to 14% Fe). |
| Zinc | |
Deficiency symptoms:
Corrective measures:
Zinc sources: Zinc sulfate, Zinc carbonate, Zinc chloride, Zinc chelate, Zinc oxide. Zinc toxicity symptoms: Excess zinc commonly produces iron chlorosis in plants. |   |
| Aluminium | |
 | Toxicity symptoms:
|
| Boron | |
Deficiency symptoms:
Boron sources: Anhydrous borax, Fertilizer borate, borax. Toxicity symptoms:
Corrective measures:
|   |
| Copper | |
 | Deficiency symptoms:
Copper sources: Cupric sulfate, Cu oxide |
| Manganese | |
Deficiency symptoms:
Manganese sources: Mn sulfate,Mn chloride Toxicity symptoms:
Corrective measures:
|   |
| Silicon | |
 | Deficiency symptoms:
Calcium silicate, potassium silicate, blast furnace slag. |
| Sodium |
Toxicity symptoms:
Corrective measures: Soil application of gypsum at 100-200 kg/ha and leach with water. |
| Sulphur |
Toxicity symptoms:
|
| Top |
| Organic Manures |
| (1) Green Manuring (2) Biofertilizer (3) Organic Manuring Practices |
| Green Manuring | |||||||||||||||||||
| Green Manure | |||||||||||||||||||
|  | ||||||||||||||||||
| Green Leaf Manures | |
    |
|
| Advantages of green Manuring |
|
| Biofertilizer |
|
| Azolla | |
|  |
| Blue green algae | |
 |
|
| Azotobacter | |
|  |
| Azospirillium | |
 | Inoculation with Azospirillum promotes early tillering and also the growth of rice and significantly increases filling rate of grain and the grain weight per plant at harvest. |
| Phosphobacteria | |
|  |
| Azospirillium,Phosphobacteria,Azotobacter | ||||||||||||
Number of packets/hectare is
|
| Mycorrhiza | |
 |
|
| Phosphate Solubilisers | |
|  |
| Methods of application of Biofertilizer | |
 |
|
| Seed Treatment | |
|  |
| Seedling Root Dip | |
 |
|
| Main field Preparation | |
| Four packets of the inoculant is mixed with 20 kgs of dried powdered farm yard manure and broadcast in one acre of main field just before transplanting. |  |
| Combained application of Bacterial Biofertilizers | |
 | Phosphobacteria can be mixed with Azospirillum. The inoculants should be mixed in equal quantities and applied as mentioned above. |
| Organic Manuring practices |
| TamilNadu | |
|   |
| Kerala | |
 |
|
| Karnataka | |
Drill sown paddy :
Sow green manure seeds of Sesbania rostrata (@ 25kg/ha) along with the application of entire P2O5 recommended for paddy, eight weeks before transplanting of paddy, then in situ incorporate the green manure crop by carrying out hodta operation ( Planking) seven weeks after sowing. Transplant paddy seedlings after one week of incorporation along with the application of 50% recommended nitrogen for paddy. |   |
| Top |
| Fertilizer Requirements |
| (1) Fertilizer Requirements |
| These products are quick acting, even in cool soils and they are inexpensive. They are the most effective means of increasing crop production and supplement nutrient supply in the soil, especially to correct yield-limiting factors. |
 (1) a)Tamil Nadu (1) a)Tamil NaduTransplanted Puddled Low Land Rice | |
Blanket recommendation (Kg/ha) – 150:50:50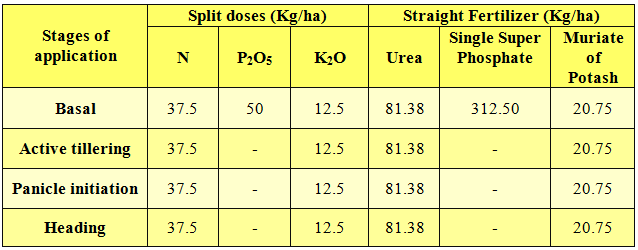 | |
| Direct wet seeded puddled lowland rice, Dry seeded rainfed un-puddled lowland rice and Rainfed upland rice | |
Blanket recommendation (Kg/ha) – 50:25:25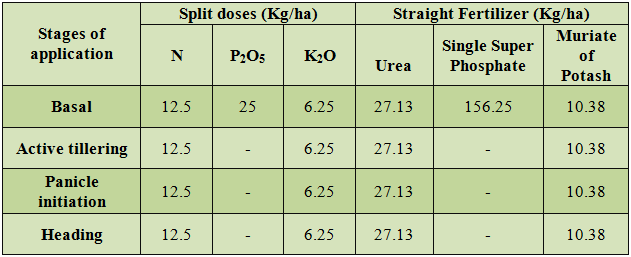 | |
| Semidry System-Dry seeded rice in un-puddled low land | |
Blanket recommendation (Kg/ha) –:75:25:37.5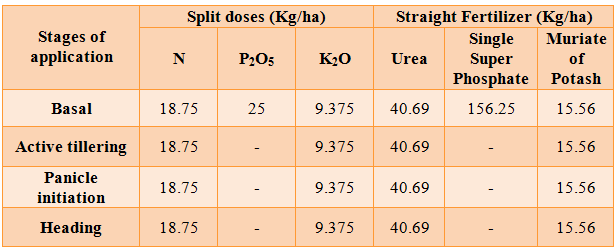 | |
 (b) Kerala (b) Kerala | |
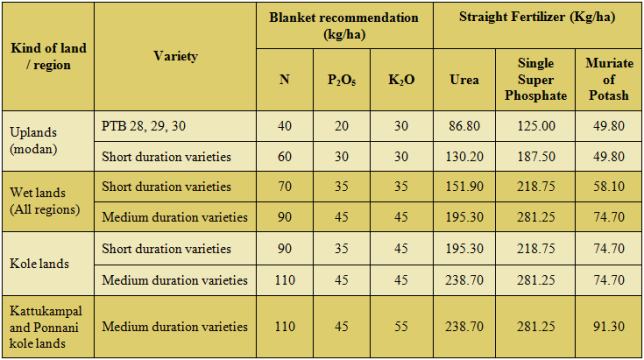 1. For short duration varieties, N is applied in three equal splits viz., basal, active tillering, and active panicle initiation stages. The recommended P is fully applied as basal. K is applied in two equal splits viz., basal and active panicle initiation stages. 2. For medium and long duration varieties, N are applied in two equal splits viz., basal and active panicle initiation stages. The recommended P is fully applied as basal. K is applied in two equal splits viz., basal and active panicle initiation stages. 3. For direct seeded crop, the basal application should be done one week after sowing. | |
 (c) Karnataka (c) Karnataka | |
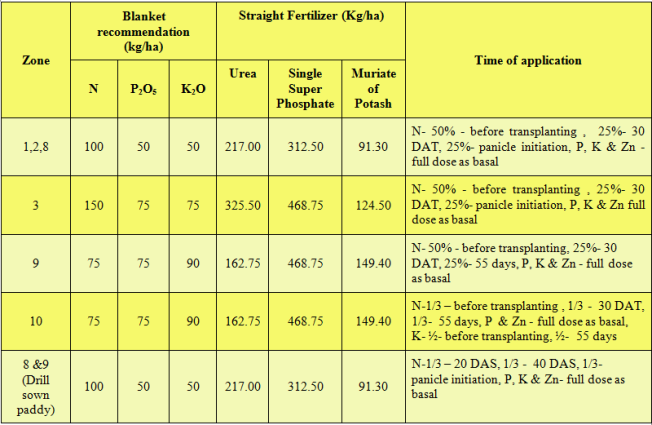 Zone 2 - North Eastern Dry Zone Zone 3 - Northern Dry Zone Zone 4 - Central Dry Zone Zone 5 - Eastern Dry Zone Zone 6 - Southern dry Zone Zone 7- Southern Transition Zone Zone 8 - Northern Transition Zone Zone 9 - Hill Zone Zone 10 - Coastal Zone | |
 (2) Method of Fertilizer application (2) Method of Fertilizer applicationSoil application | |
Basal application
Top dressing Apply 25 % recommended dose of N and K each as top dressing at active tillering, panicle initiation and heading stages. |  |
| Foliar Nutrition in paddy | |
 |
|
| Growth Regulators | |
|  |
| Top | |
| Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) | |
 | Integrated nutrient management (INM) aims at reducing the chemical fertilizer applied and improving its efficiency through combined use of different sources of plant nutrients such as Fertilizers, 1. Organic manures, 2. Green manures, 3. Crop residues, 4. Biofertilisers and 5.Industrial wastes / soil conditioners in balanced proportions, depending on their availability and suitability in a specific rice ecosystem. Sources of nutrients: 1. Organic manures / compost – 12.5 t of FYM 2. Green manures / green leaf manures / crop residues - 6.25 t/ha 3. Fertilizers – Apply blanket recommendation as per the ecosystem. Biofertilizers: 1. Azolla –as green rmanure @ 6t /ha, as dual crop (0.5 t/ha) in 7 DAT 2. Blue green algae - 10 kg/ha on 10 DAT 3. Azotobacter /Azospirillium /Phosphobacteria - 10 packets (soil application) 4. Azophos – 20 packets (soil application) Micronutrients:
|